π-PrimeNovo: an accurate and efficient non-autoregressive deep learning model for de novo peptide sequencing
Jan 2, 2025· ,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,·
1 min read
,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,·
1 min read
Xiang Zhang
Tianze Ling
Zhi Jin
Sheng Xu
Zhiqiang Gao
Boyan Sun
Zijie Qiu
Jiaqi Wei
Nanqing Dong
Guangshuai Wang
Guibin Wang
Leyuan Li
Muhammad Abdul-Mageed
Laks v. S. Lakshmanan
Fuchu He
Wanli Ouyang
Cheng Chang
Siqi Sun
Abstract
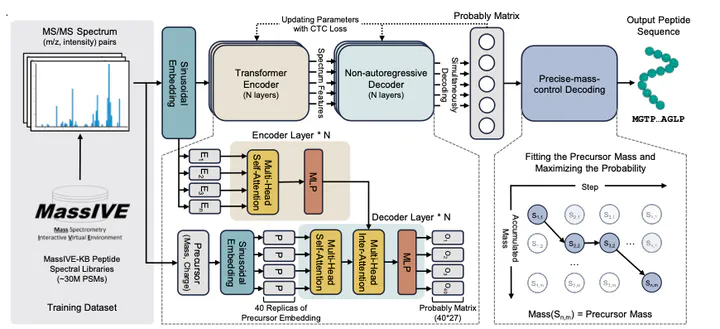
Peptide sequencing via tandem mass spectrometry (MS/MS) is essential in proteomics. Unlike traditional database searches, deep learning excels at de novo peptide sequencing, even for peptides missing from existing databases. Current deep learning models often rely on autoregressive generation, which suffers from error accumulation and slow inference speeds. In this work, we introduce π-PrimeNovo, a non-autoregressive Transformer-based model for peptide sequencing. With our architecture design and a CUDA-enhanced decoding module for precise mass control, π-PrimeNovo achieves significantly higher accuracy and up to 89x faster inference than state-of-the-art methods, making it ideal for large-scale applications like metaproteomics. Additionally, it excels in phosphopeptide mining and detecting low-abundance post-translational modifications (PTMs), marking a substantial advance in peptide sequencing with broad potential in biological research.
Type
Publication
Nature Communications 16, No. 267
Add the publication’s full text or supplementary notes here. You can use rich formatting such as including code, math, and images.